엄밀히 Design Pattern은 아니지만 Bridge pattern과 비슷한 계층 개념인 PIMPL(Point to implementation)에 대해서 알아보자.
PIMPL의 장점
1. 컴파일 속도를 향상시킨다.
2. 완벽한 정보 은닉이 가능하다. 헤더 파일을 감출 수 있다.
이러한 개념을 예제를 통해 알아보자. 다음은 Point 클래스와 이에 대한 구현의 간단한 예이다.
// Point1.h
class Point
{
int x, y;
public:
Point(int a = 0, int b = 0);
void Print() const;
};
// Point1.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Point1.h"
using namespace std;
Point::Point(int a, int b) :x(a), y(b) {}
void Point::Print() const
{
cout << x << ", " << y << endl;
}
// Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Point1.h"
int main()
{
Point p(1, 2);
p.Print();
}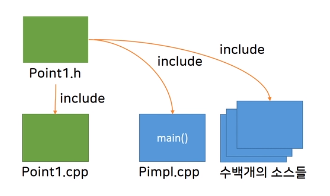
Point 클래스에 대한 header, cpp와 Main 파일로 구성되어있다. 이 예제에서 사용자의 요구나 개발자의 필요에 의해 Point에 기능을 추가해야 한다면 어떻게 해야할까? 아주 간단하게 다음과 같이 Point1.h에서 멤버 데이터를 추가 해줄 수 있겠다.
class Point
{
int x, y;
int debug; // 멤버 데이터의 추가 -> 컴파일 한다면? -> 이 파일을 include한 모든 파일이 리빌드가 된다.
public:
Point(int a = 0, int b = 0);
void Print() const;
};본 예제 안에서는 가장 간단한 구현 방법일 수 있으나 만약 이 클래스가 이미 많은 곳에서 사용중인 것이라면 이야기가 달라진다. 구현 자체는 간단했지만, Point1.h를 include한 모든 파일에서 다시 컴파일이 발생하므로 컴파일 시간이 굉장히 많이 늘어나게 된다. 이러한 문제를 해결할 수 있는 방법이 바로 PIMPL이다.
PIMPL
위의 예제를 개선하기 위해서 PointImpl과 Main 사이에 하나의 계층을 추가한다.
이 예제에서 PointImpl은 이전 예제에서 Point1을 대채한다.
// PointImpl.h
class PointImpl
{
int x, y;
// 사용자 요구에 의해서 기능추가된다면?
// 다시 컴파일 되는 대상은
// PointImpl, Point2 뿐이다.
int debug;
public:
PointImpl(int a = 0, int b = 0);
void Print() const;
};// PointImpl.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "PointImpl.h"
using namespace std;
PointImpl::PointImpl(int a, int b) :x(a), y(b) {}
void PointImpl::Print() const
{
cout << x << ", " << y << endl;
}
// Point2.h
class PointImpl;
class Point
{
PointImpl* pImpl;
public:
Point(int a = 0, int b = 0);
void Print() const;
};// Point2.cpp
#include "PointImpl.h"
#include "Point2.h"
Point::Point(int a, int b)
{
pImpl = new PointImpl(a, b);
}
void Point::Print() const
{
pImpl->Print();
}#include <iostream>
#include "Point1.h"
int main()
{
Point p(1, 2);
p.Print();
}
위 구현 내용은 아래의 그림과 같다. PointImpl.h 가 변경되더라도 다시 컴파일되는 범위는 PointImpl.cpp와 Point2.cpp로 재한된다. 게다가 이것을 라이브러리로 사용자에게 제공하는 경우, Point.h와 라이브러리 파일을 제공하면 되므로 PointImpl.h의 내용도 완전히 감출 수 있어 완전한 정보은닉의 장점이 한가지 더 있다.
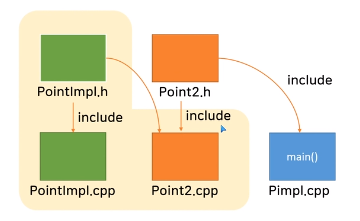
정리
PIMPL -> 중간계층의 추가 -> 컴파일 속도 빨라짐 -> 정보 은닉 효과
'프로그래밍 이야기 > C++ 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Design Pattern] Container (0) | 2021.02.05 |
|---|---|
| [Design Pattern] Observer (관찰자) (0) | 2021.02.04 |
| [Design Pattern] Bridge (0) | 2021.02.02 |
| [DesignPattern] Facade (0) | 2021.01.19 |
| [C++]Design Pattern - STL과 Adapter (0) | 2020.12.30 |
